March 6, 2025
Knowledge-guided diffusion model for 3D ligand-pharmacophore mapping
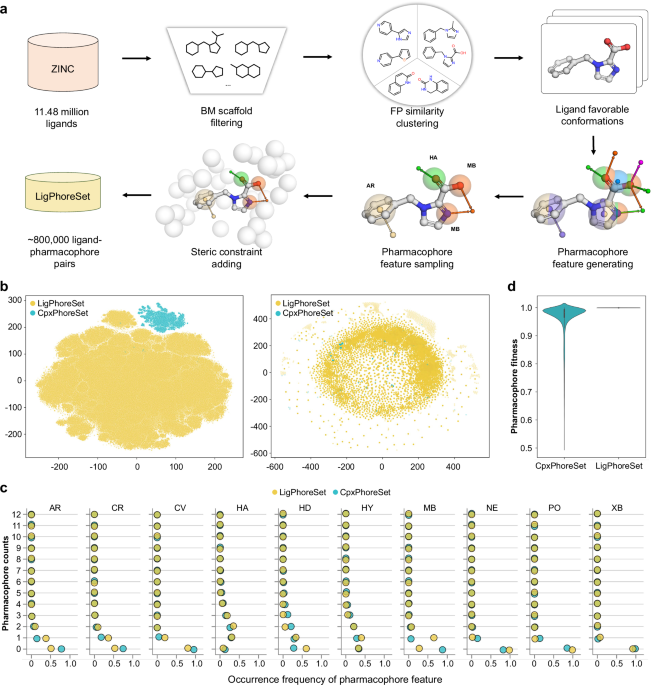
Dataset construction We constructed two 3D ligand-pharmacophore pair datasets, CpxPhoreSet and LigPhoreSet, for LPM learning, by using the enhanced version of AncPhore23. CpxPhoreSet was established by analyzing a total of 19,443 protein-ligand complex structures collected in PDBBind (version 2020)47,48. We followed a time-split scheme14 and divided PDBBind into train (16,379 entries), validation (968 entries), and test (363 entries) sets. The train and validation set were used to establish the CpxPhoreSet and the remaining test set was used for performance evaluation. For each complex structure, AncPhore was used to generate one pharmacophore model considering 10 pharmacophore feature types (HD, HA, MB,