JavaScript is a dynamically typed language, meaning you don’t have to specify a variable’s type explicitly. However, understanding data types is crucial for writing efficient and bug-free code.In this blog, we’ll explore JavaScript’s data types, their characteristics, and how they work.
Primitive Data Types
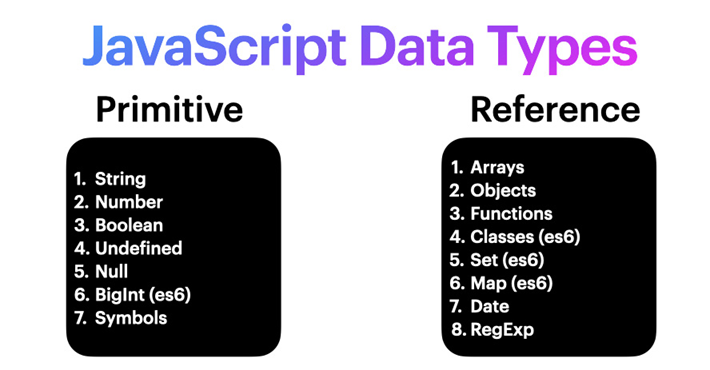
JavaScript has seven primitive data types, which are immutable and stored by value.
1. String
A string represents textual data enclosed in quotes.
let name = "Ramyasree";
let greeting = 'Hello, world!';
Strings can be manipulated using various methods like length, toUpperCase(), toLowerCase(), concat(), etc.
2. Number
JavaScript uses a single Number type to represent both integers and floating-point numbers.
let age = 25;
let price = 99.99;
Special numeric values include Infinity, -Infinity, and NaN (Not-a-Number).
3. Boolean
A Boolean represents a logical entity that can have only two values: true or false.
let isLoggedIn = true;
let hasAccess = false;
4. Undefined
A variable that has been declared but has not been assigned a value is undefined.
let x;
console.log(x); // undefined
5. Null
null is an intentional absence of any value.
let y = null;
console.log(y); // null
6. BigInt
BigInt is used for integers larger than Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER.
let bigNumber = 123456789012345678901234567890n;
console.log(bigNumber);
7. Symbol
Symbols are unique and immutable primitive values used as object keys.
let sym1 = Symbol('id');
let sym2 = Symbol('id');
console.log(sym1 === sym2); // false
Non-Primitive (Reference) Data Types
Non-primitive data types are objects and are stored by reference.
1. Array
Arrays are special types of objects used to store lists of values.
let colors = ["red", "green", "blue"];
console.log(colors[1]); // green
2. Object
Objects are collections of key-value pairs.
let person = {
name: "Alice",
age: 30,
isStudent: false
};
console.log(person.name); // Alice
3. Function
Functions are also objects in JavaScript and can be assigned to variables.
function greet() {
return "Hello!";
}
console.log(greet()); // Hello!
4.Classes
Templates for creating objects.
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
5.Set
A collection of unique values.
let uniqueNumbers = new Set([1, 2, 3, 3]);
6.Map
A collection of key-value pairs where keys can be any data type.
let map = new Map();
map.set("name", "Alice");
7.Date
Used to work with date and time
let today = new Date();
8.RegExp
Used for pattern matching.
let regex = /hello/i;
Conclusion
Understanding JavaScript data types is essential for writing robust applications. By knowing how primitive and reference types work, you can avoid unexpected bugs and improve performance.
If you found this helpful, share your thoughts in the comments or follow me for more JavaScript insights!
Happy Coding!!